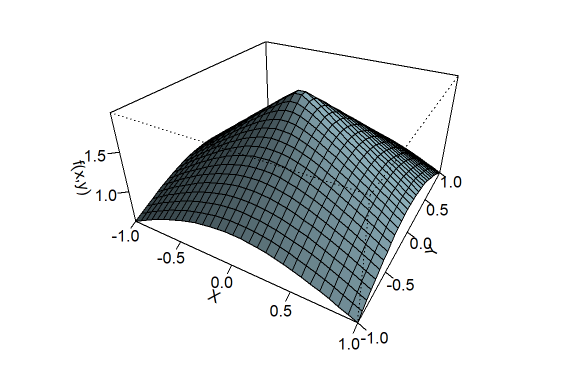
Section 15 Functions of Several Variables In this section we want to go over some of the basic ideas about functions of more than one variable First, remember that graphs of functions of two variables, z = f (x,y) z = f ( x, y) are surfaces in three dimensional space For example, here is the graph of z =2x2 2y2 −4 z = 2 x 2 2 y 2 − 4Free functions and graphing calculator analyze and graph line equations and functions stepbystep This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience By using this website, you agree to our Cookie Policy We are given the quadratic function y = f (x) = (x 2)2 For the family of quadratic functions, the parent function is of the form y = f (x) = x2 When graphing quadratic functions, there is a useful form called the vertex form y = f (x) = a(x −h)2 k, where (h,k) is the vertex Data table is given below (both for the parent function and the given function)
Graph Of A Function In 3d
F x y x 2 y 2 graph
F x y x 2 y 2 graph-C < 0 moves it downThe tangent plane to the surface at A contains the tangent line to Cat A



What Are The Extrema And Saddle Points Of F X Y X 2 Xy Y 2 Y Socratic
Hence evaluate Delta=f_(x x)f_(yy)f_(xy)^2 at each of these points Determine the nature of the extrema;Algebra Graph f (x)=2 f (x) = 2 f ( x) = 2 Rewrite the function as an equation y = 2 y = 2 Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is y = m x b y = m x b, where m m is the slope and b bCurves in R2 Three descriptions (1) Graph of a function f R !R (That is y= f(x)) Such curves must pass the vertical line test Example When we talk about the \curve" y= x2, we actually mean to say the graph of the function f(x) = x2That is, we mean the set
The graph of a function f(x,y) with domain D is a collection of points (x,y,z) in space such that z = f(x,y), (x,y) ∈ D The domain D is a set of points in the xy plane The graph is then obtained by moving each point of D parallel to the z axis by an amountThe graph crosses Y axis when x equals 0 substitute x = 0 to x^3/6 9*x/2 2 $$\left( \frac{0^{3}}{6} \frac{0 \cdot 9}{2}\right) 2$$ The resultThis tool graphs z = f (x,y) mathematical functions in 3D It is more of a tour than a tool All functions can be set different boundaries for x, y, and z, to maximize your viewing enjoyment This tool looks really great with a very high detail level, but you may find it more comfortable to use less detail if you want to spin the model
If f(2)=3 and f'(2)=5 find the equation of the tangent line and the normal line to the graph of y=f(x) Asked by jsmoore Mathematics Answered Out if f(2)=3 and f'(2)=5 find the equation of the tangent line and the normal line to the graph of y=f(x)Mathematics 2 months ago Give AnswerGet the free "Surface plot of f(x, y)" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle Find more Engineering widgets in WolframAlphaIn mathematics, an inverse function (or antifunction) is a function that "reverses" another function if the function f applied to an input x gives a result of y, then applying its inverse function g to y gives the result x, ie, g(y) = x if and only if f(x) = y The inverse function of f is also denoted as As an example, consider the realvalued function of a real variable given by f(x



Calculus Iii Functions Of Several Variables



Graphing Quadratic Functions
Let us start with a function, in this case it is f(x) = x 2, but it could be anything f(x) = x 2 Here are some simple things we can do to move or scale it on the graph We can move it up or down by adding a constant to the yvalue g(x) = x 2 C Note to move the line down, we use a negative value for C C > 0 moves it up;Sketch the graph of y = f (x 2) 1, where f (x) = x 2 for 2 < X < 2 Question Sketch the graph of y = f (x 2) 1, where f (x) = x 2 for 2 < X < 2 check_circle1)Graph f(x)=(x^2 4)/(x 2) using a graphing calculator Using a standard window with the trace feature, trace the graph to x=2 What happens?



2




The Graph Of X Y 2x Y2 Is Shown Below F X Y 2x Y Homeworklib
Find stepbystep Calculus solutions and your answer to the following textbook question Suppose the line tangent to the graph of f x=2 is y=4x1 and suppose y=3x2 is the line tangent to the graph of g at x=2 Find an equation of the line tangent to the following curves at x=2 a y=f(x)g(x), b y=$\frac { f ( x ) } { g ( x ) }$Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, musicThe trace of the graph of z f x y x 2 2 y 2 on the plane z 2 is which of the The trace of the graph of z f x y x 2 2 y 2 on the School University of Texas;



Shivajicollege Ac In



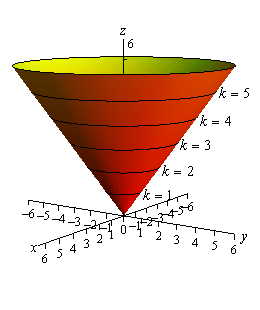
Z X 2 Y 2
Para hallar los extremos hay que resolver la ecuación $$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$ (la derivada es igual a cero), y las raíces de esta ecuación serán los extremos de esta funciónWhy is the graph a line without a vertical asymptote at x=2?X^2y^2=0 (xy)(xy)=0 Now because of this, your graph will be where either xy=0, and where xy=0 As you can tell, those are going to be a pair of lines, intersecting at (0,0) The rest is an exercise for the student




Plotting Functions And Graphs In Wolfram Alpha Wolfram Alpha Blog



2
Select a few x x values, and plug them into the equation to find the corresponding y y values The x x values should be selected around the vertex Tap for more steps Replace the variable x x with − 1 1 in the expression f ( − 1) = ( − 1) 2 − 2 f ( 1) = ( 1) 2 2 Simplify the resultCourse Title CALCULUS 408;Answer (1 of 14) f(x) means that you replace every 'x' by x f(x) means that you change or of f(x) It is the same function, if the function only has x with odd exponents like x, x^3, x^5, x^(7) etc However, if you have anyhing else, f(x) is not f(x) For example, f(x)= x^2 f(x



2



A The Graph Of F X Y X 2 Y 2 The Point 0 0 Is A Download Scientific Diagram
View my channel http//wwwyoutubecom/jayates79Type Homework Help Uploaded By bunnyyoon Pages 7 This preview shows page 5 7 out of 7 pagesFree tangent line calculator find the equation of the tangent line given a point or the intercept stepbystep



Graph Of A Function In 3d
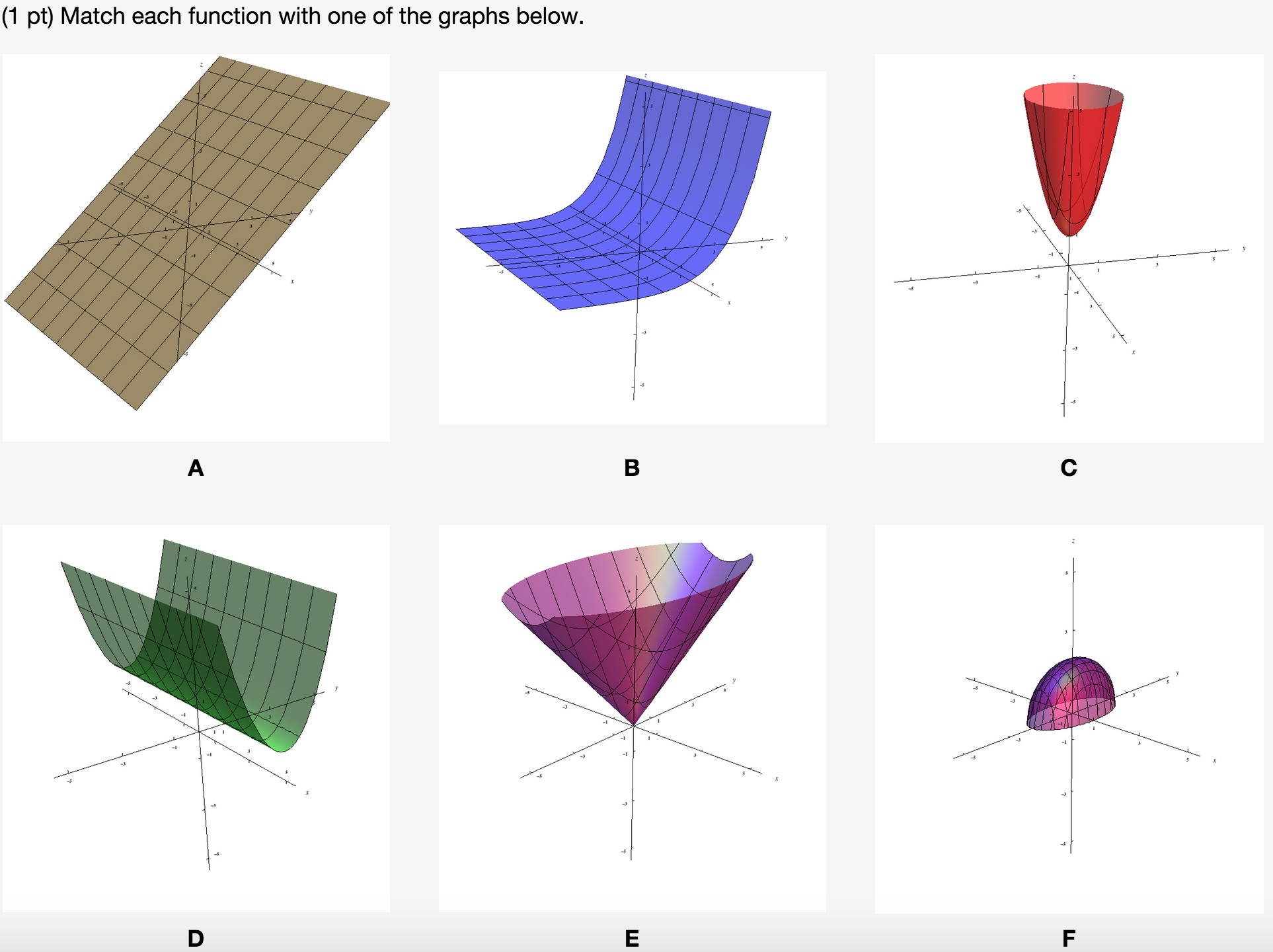



Solved Match Each Function With One Of The Graphs Below 1 Chegg Com
Graph the parent quadratic (y = x^2) by creating a table of values using select x values The graph of this parent quadratic is called a parabolaNOTE AnyExperts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area We review their content and useAlong the line y = mx, f(x,y) = m2x3/(x2 m4x4) As x approaches 0 this expression approaches 0 as well So along every line through the origin f(x,y) approaches 0 Now suppose we approach the origin along x = y2 Then f(x,y) = y2y2 y4 y4 = y4 2y4 = 1 2, so the limit is 1/2 Looking at figure 1421, it is apparent that there is a ridge




Problem 3 Define The Function 2 0 If Z Y 10 0 If A Y 0 0 F X V A Graph The Homeworklib



2
Thus, "x 2 y 2" is written "x*x y*y" or "x^2 y^2" 2 For example, f(x,y) = x 2 y 2 will be graphed as in the image below 3 You may wish to save the graph image as a file on your PC it will use about 35 KBAnd this is for X, divided by two Well, black graph we have Why, Zurich and execute on for the bread craft We have 000 plus zero would just give us your at this point, we have one plus zeroSelect a few x x values, and plug them into the equation to find the corresponding y y values The x x values should be selected around the vertex Tap for more steps Replace the variable x x with 0 0 in the expression f ( 0) = ( 0) 2 − 2 ⋅ 0 − 2 f ( 0) = ( 0) 2 2 ⋅ 0 2 Simplify the result




If X X1 X2 Represents A Point In A Subset A Of Rn And F X Is Exactly One Point In Rm Then We Say That F




13 1 Functions Of Multiple Variables Mathematics Libretexts
Steps for Solving Linear Equation y = f ( x ) = 2 ( x 1 ) y = f ( x) = 2 ( x 1) Use the distributive property to multiply 2 by x1 Use the distributive property to multiply 2 by x 1 y=2x2 y = 2 x 2 Swap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand sideQuestion Sketch the graph of the function f(x,y)=x^2 4y^2 1 This problem has been solved!Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor
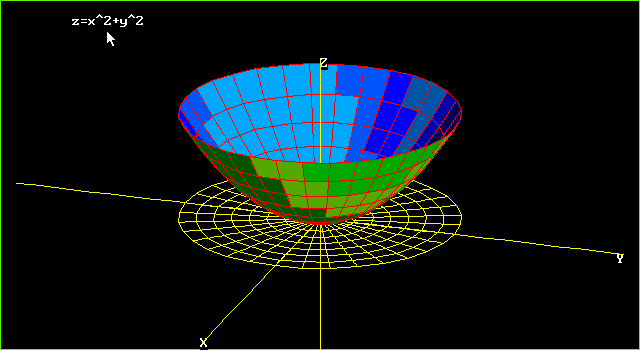



Graphs Of Surfaces Z F X Y Contour Curves Continuity And Limits
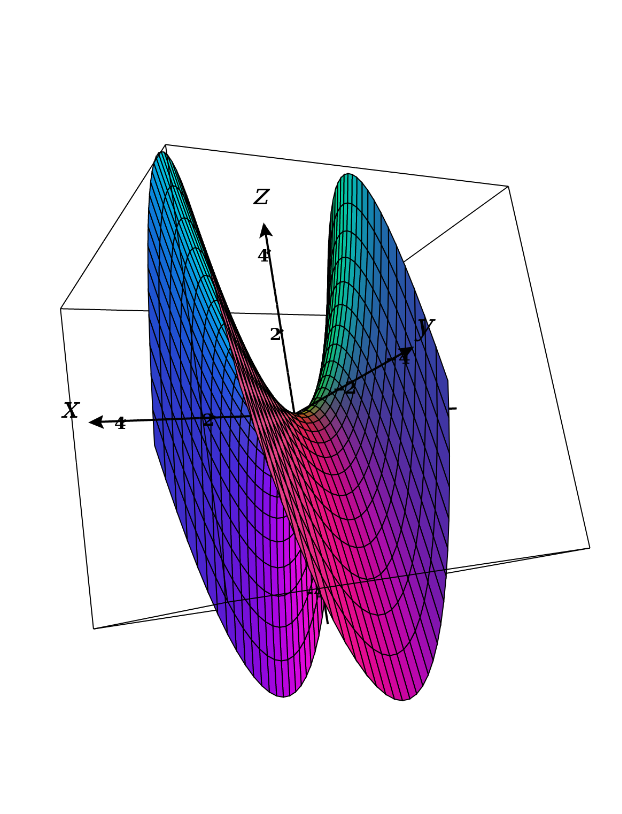



Sketch The Graph Of F F X Y X Y Quizlet
Transcribed image text Question 2 (2 points) (Sec 25) The graph of y = f(x) is given below 4 y=f(x) 3 2 3 V 2 3 4 Use the graph of y = f(x) to determine which of the following graphs is the graph of my = f(x 2) and (m) y = f(x) 2 Graph 1 3 sire2learncom ser accompUque Hartrame autod Bogi 127 39 crot=0 25 (23, 25) F1 imit Time Left2 Why is there a "break" in the line at x=2?2y=x2 Geometric figure Straight Line Slope = 1000/00 = 0500 xintercept = 2/1 = 0000 yintercept = 2/2 = 1 Rearrange Rearrange the equation by subtracting what is to the Transforming points from function



0 3 Visualizing Functions Of Several Variables



Graphing Quadratic Functions
Consider f (x) with the following graph y 2 2 (a) List all the xvalues where the derivative doesn't exist and specify the type of non differentiability at each (b) Specify the Domain, the Region of Continuity, and the Region of Differentiability of this functionSee the answer See the answer See the answer done loading Sketch the graph of the function f(x,y)=x^2 4y^2 1 Expert Answer Who are the experts?Use a graph of f(x) to determine the value of f(n), where n is a specific xvalueTable of Contents0000 Finding the value of f(2) from a graph of f(x)002



Chapter 7 Functions Of Two Or More Variables Calculus And Analysis




Graph The Functions F X Y X 2 Y 2 F X Y E X 2 Quizlet
how can i draw graph of z^2=x^2y^2 on matlab Learn more about surface MATLAB C/C Graphics LibraryFree math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutorGraph of z = f(x,y) New Resources Quiz Graphing Exponential Functions (Transformations Included)




Graphs And Level Curves




Graphs And Level Curves
((4))/(2*1) = 4/2 = 2 Substitute x = 2 and find the yvalue (2)^24(2) = 4 8 = 4 The vertex is found at (2, 4) Here is the graph Also, I would suggest factoring the equation to find xintercepts x(x 4) = 0 so x = 0 and x = 4 Since the graph has vertical line symmetry through its vertex, you will notice that the vertex is literallyX^2 2 y^2 = 1 Natural Language; 2 QUESTION 2 The graph of the surface f(x,y) and a curve in the surface C (black curve) through the point A are shown below Which of the following statements is true about the tangent line to the curve Cat A and the tangent plane to the surface f(x,y) at A?




Graph Of A Function Wikipedia



File F X Y Cosx 2 Cosy 2 2 Png Wikipedia
Simple transformation for y=f(x) functionTo zoom, use the zoom slider To the left zooms in, to the right zooms out When you let go of the slider it goes back to the middle so you can zoom more You can clickanddrag to move the graph around If you just clickandrelease (without moving), then the spot you clicked on will be the new center To reset the zoom to the original clickMath Input NEW Use textbook math notation to enter your math Try it



2
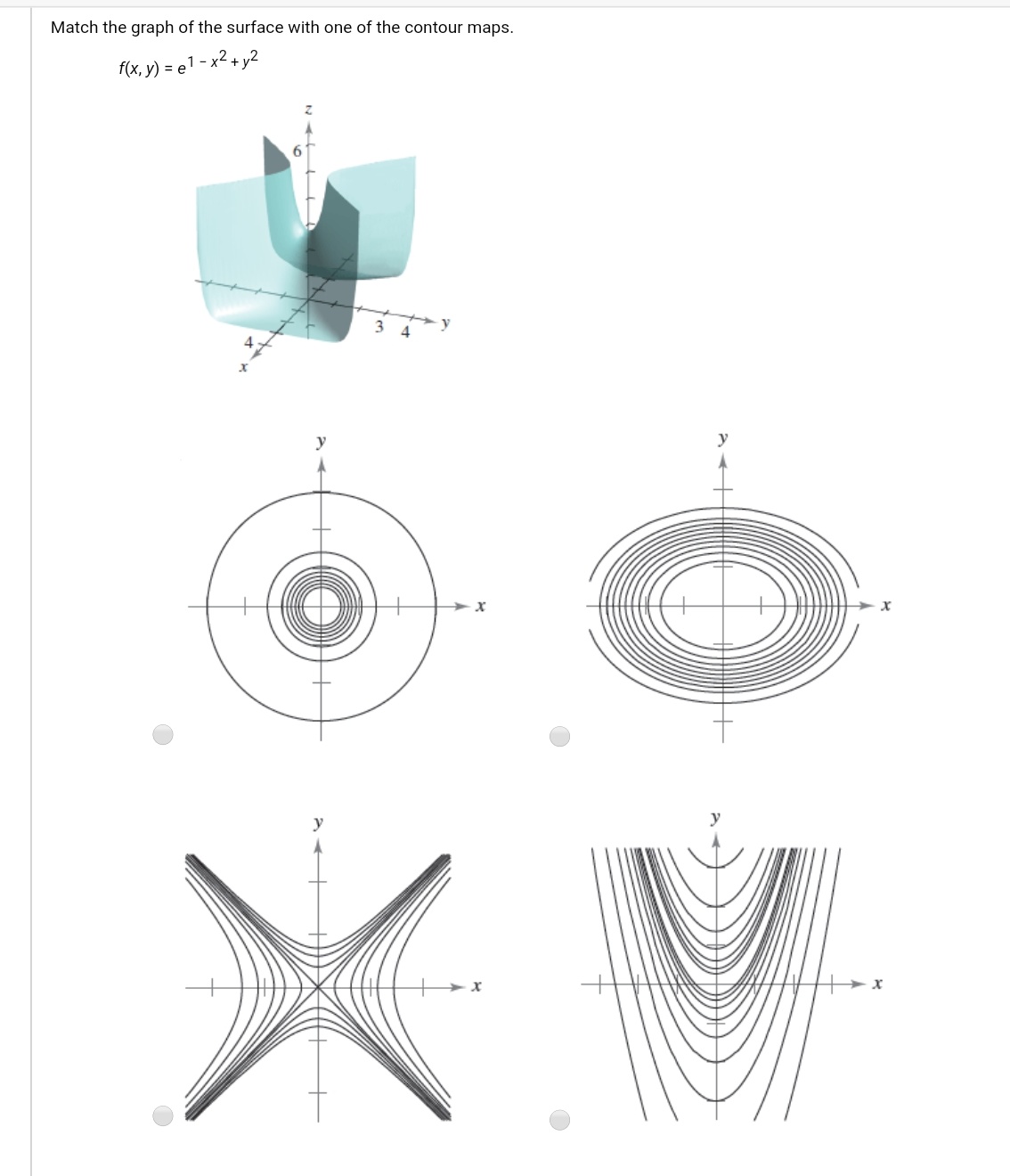



Answered Match The Graph Of The Surface With One Bartleby
{ (Delta>0, "There is minimum if " f_(x x)0), (Delta



What Are The Extrema And Saddle Points Of F X Y X 2 Xy Y 2 Y Socratic



3d Surface Plotter Academo Org Free Interactive Education




Plot F X Y X 2 Y 2 Tex Latex Stack Exchange




Sketch The Graph Of The Function F X Y Sqrt 4x 2 Y 2 Study Com



Graph Of A Function In 3d
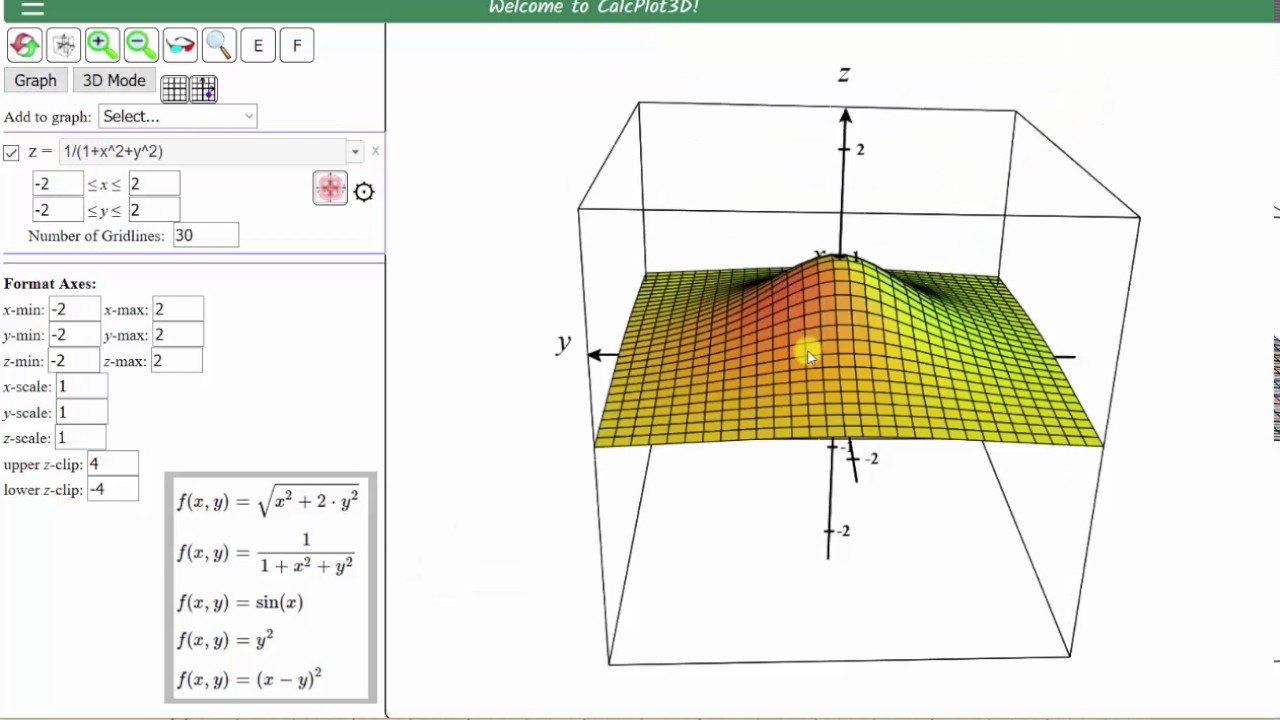



Graph A Function Of Two Variable Using 3d Calc Plotter Youtube
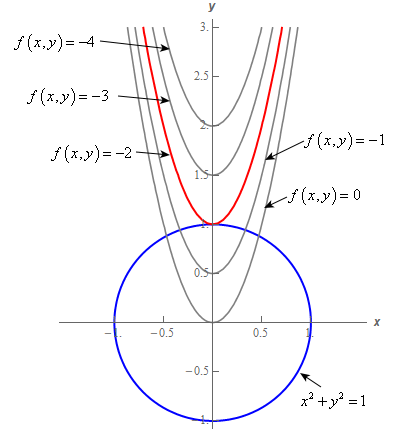



Calculus Iii Lagrange Multipliers
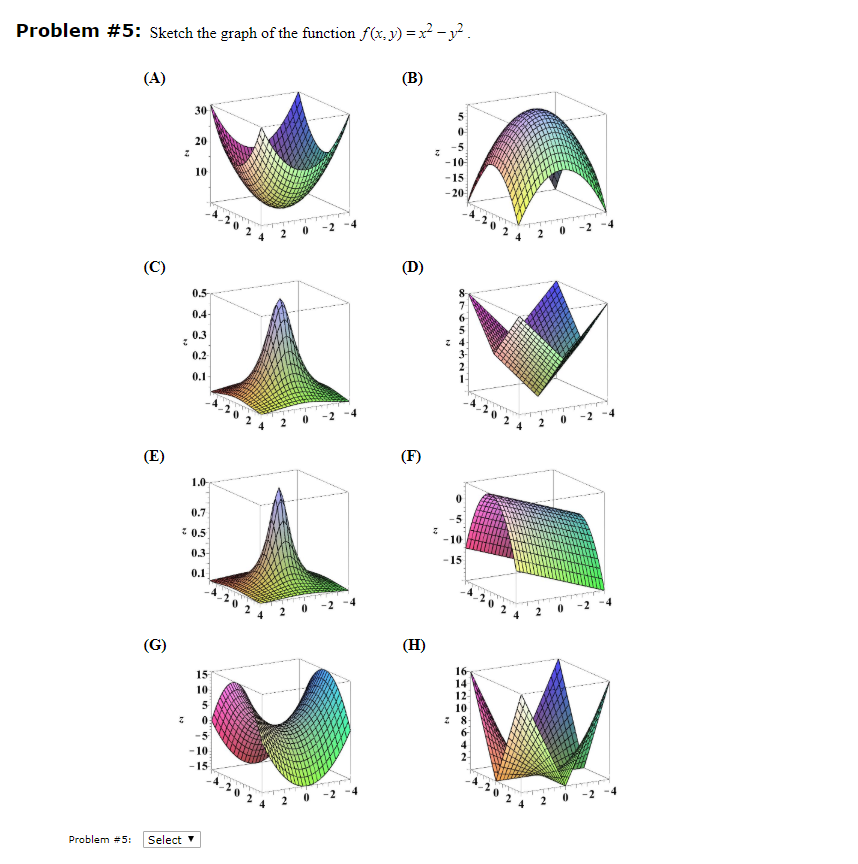



Solved Problem 5 Sketch The Graph Of The Function F X Y Chegg Com




Plot The Graph Of The Function F X Y 1 2x 2 2y 2 Study Com



21 Graph Of The Function F X Y 2xy C X 2 Y 2 C Used For L And Download Scientific Diagram
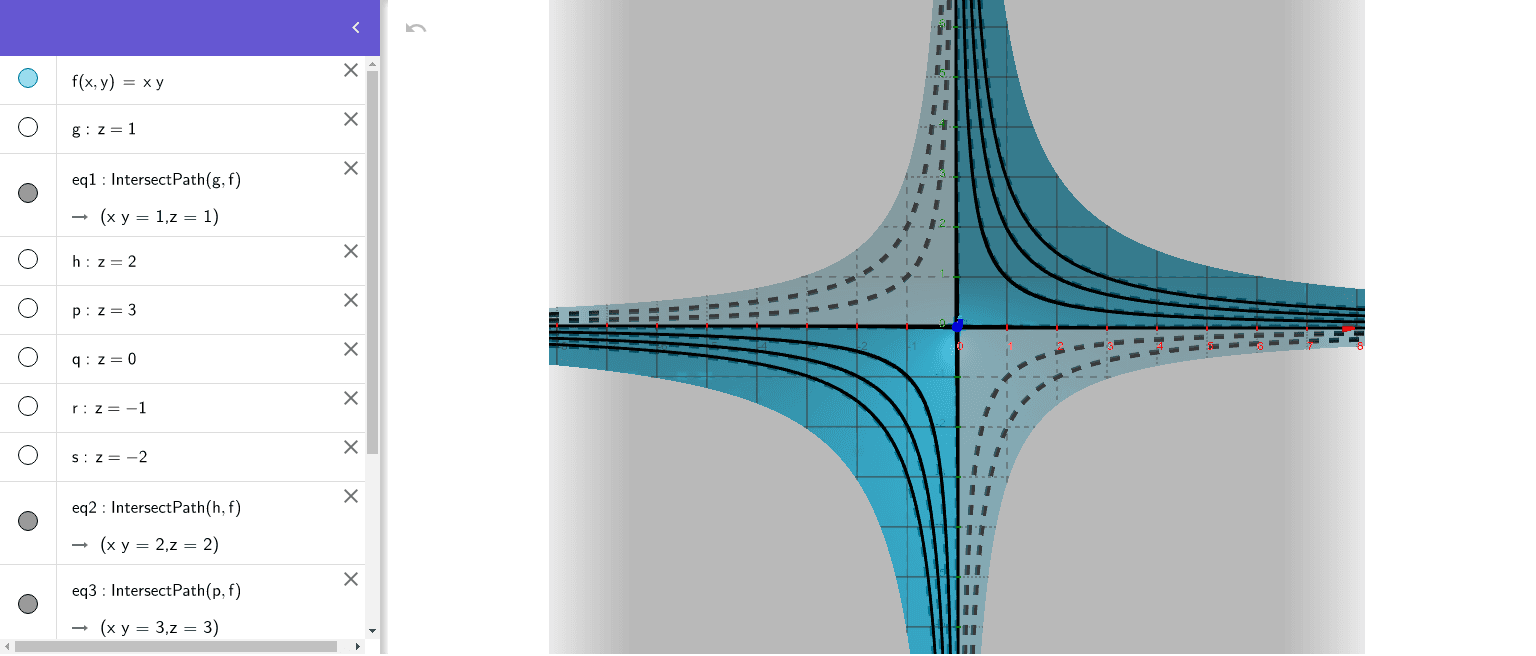



F X Y Xy Geogebra




Plotting In 3d
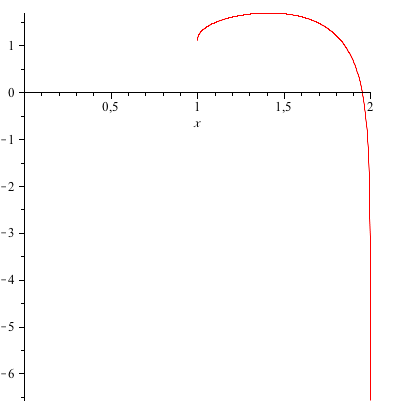



How Do You Graph F X Y Sqrt X 2 Y 2 1 Ln 4 X 2 Y 2 Socratic
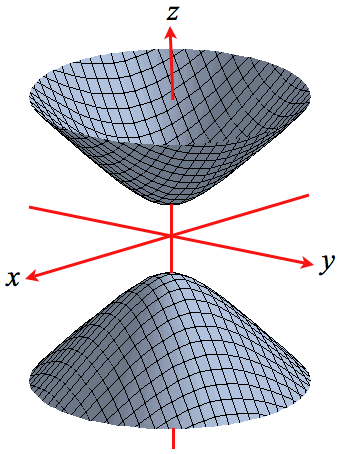



Level Surfaces




How To Find The Graphs Of The Following Multi Variable Functions F X Y Ln 1 Xy And F X Y Frac Y E X Mathematics Stack Exchange




Extrema Of Functions Of 2 Variables
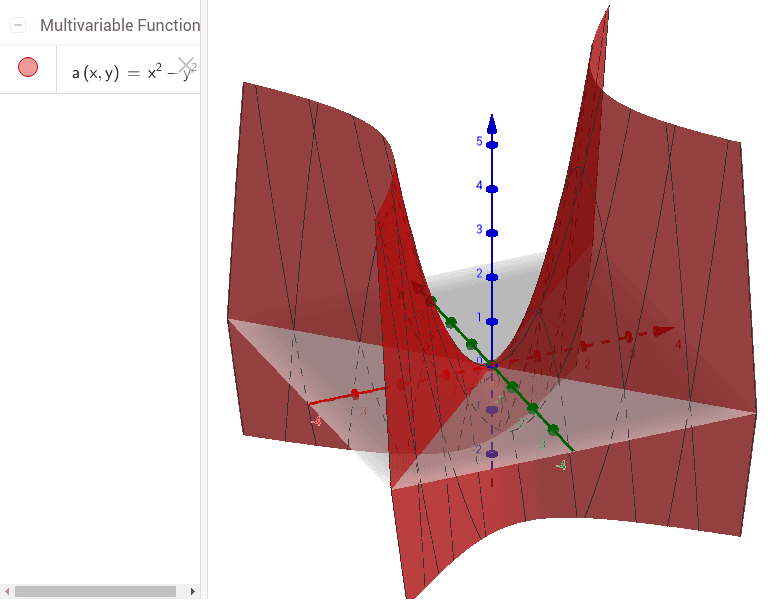



Graph Of F X 2 Y 2 Geogebra




Graph Of The Function F 1 3 1 3 2 0 For The Form F X Y Xy Download Scientific Diagram



2
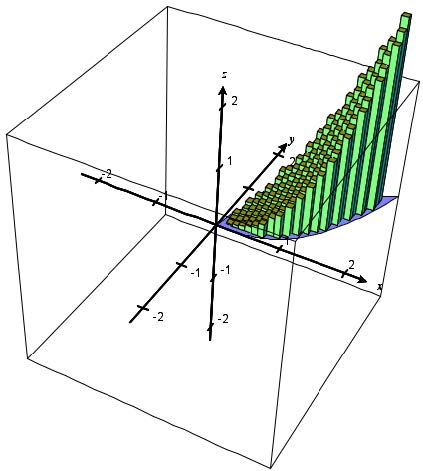



Calcplot3d An Exploration Environment For Multivariable Calculus



A Function For Which Fxy Fyx Graph Of The Function Given By F X Y X3y Xy3 X2 Y2 For X Y 0 0 And F 0 0 0 Graph Of Fx Note That The Slope In The Y Direction Through The Center Of The Graph Appears To Be Negative It Can Indeed Be Verified That Fxy 0
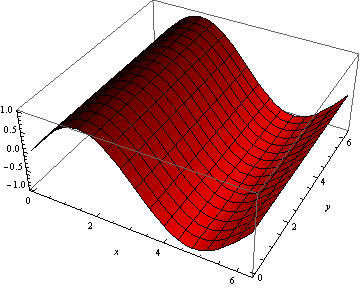



Functions And Graphing Introduction To Data Analysis For Physics



2
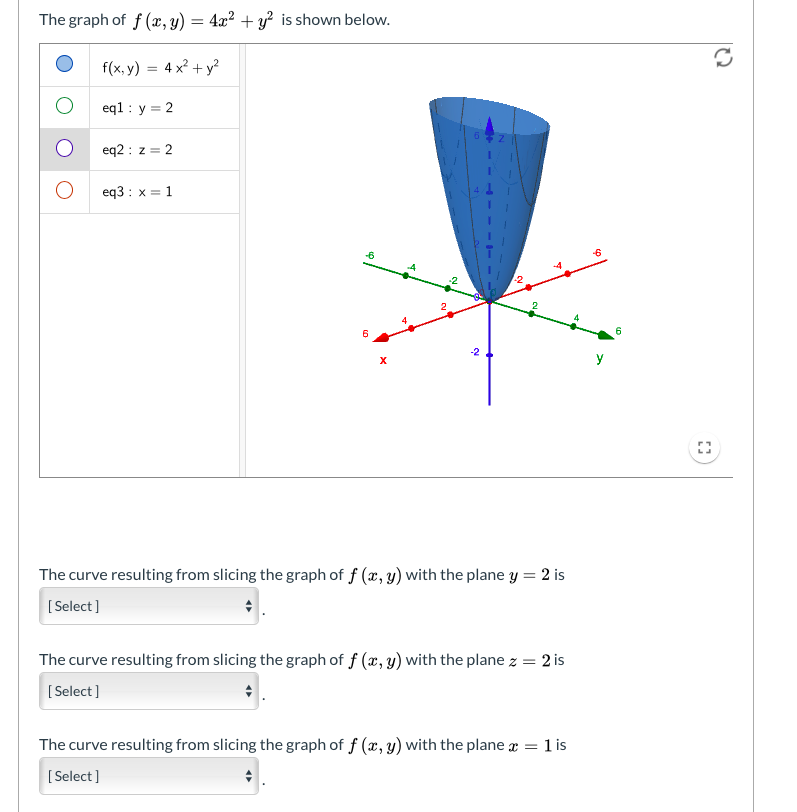



Solved The Graph Of F X Y 4 X2 Y2 Is Shown Below Chegg Com
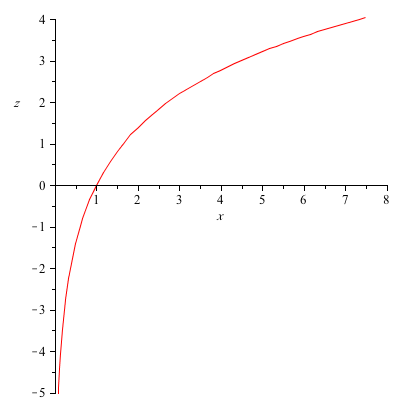



How Do You Sketch F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Socratic
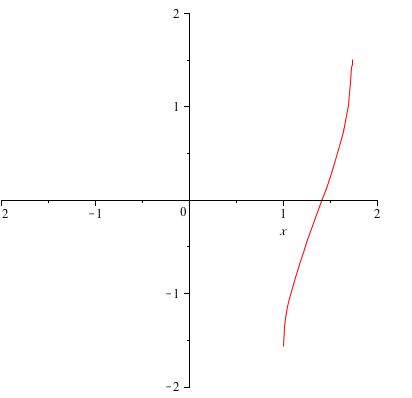



How Do You Sketch F X Y Arcsin X 2 Y 2 2 Socratic




14 1 Functions Of Several Variables Mathematics Libretexts
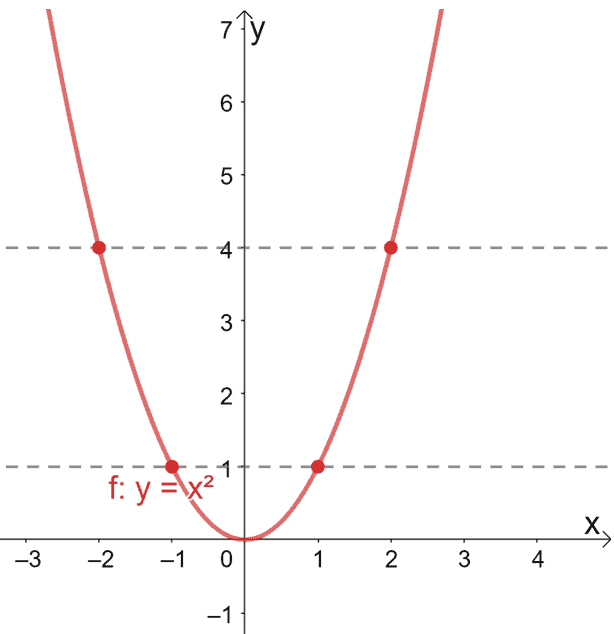



One To One Function Explanation Examples



Graph Domain And Range Of Absolute Value Functions




Graphs And Level Curves



Examples Friday Feb 21



How To Construct The Graph Of X 2 Y 2 9 Quora




Graphs And Level Curves




Sketch The Graph Of F X Y Sqrt 1 X 2 Y 2 State The Domain And Range Of The Function Study Com
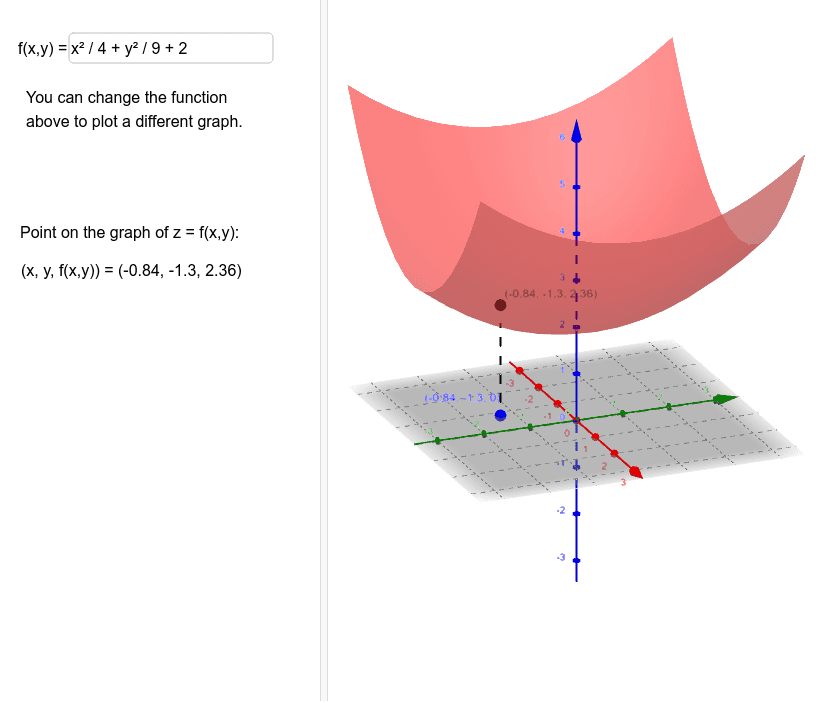



Graph Of Z F X Y Geogebra
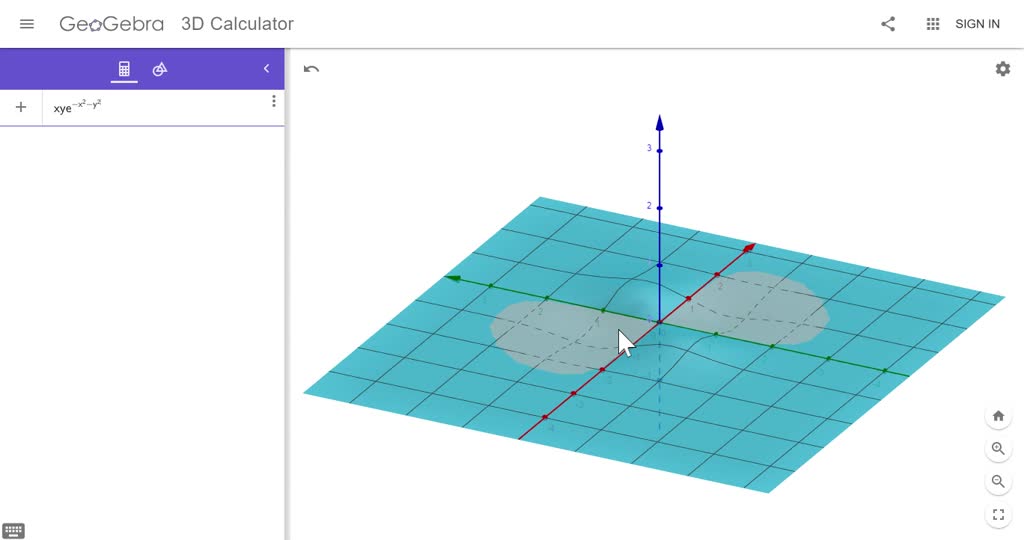



Solved Use A Graphing Utility To Sketch Graphs Of Z F X Y From Two Different Viewpoints Showing Different Features Of The Graphs F X Y X Y E X 2 Y 2




A Graph F X Y 9 X 2 Y 2 B Find The Normal Vector To The Tangent Plane For 2 1 Study Com
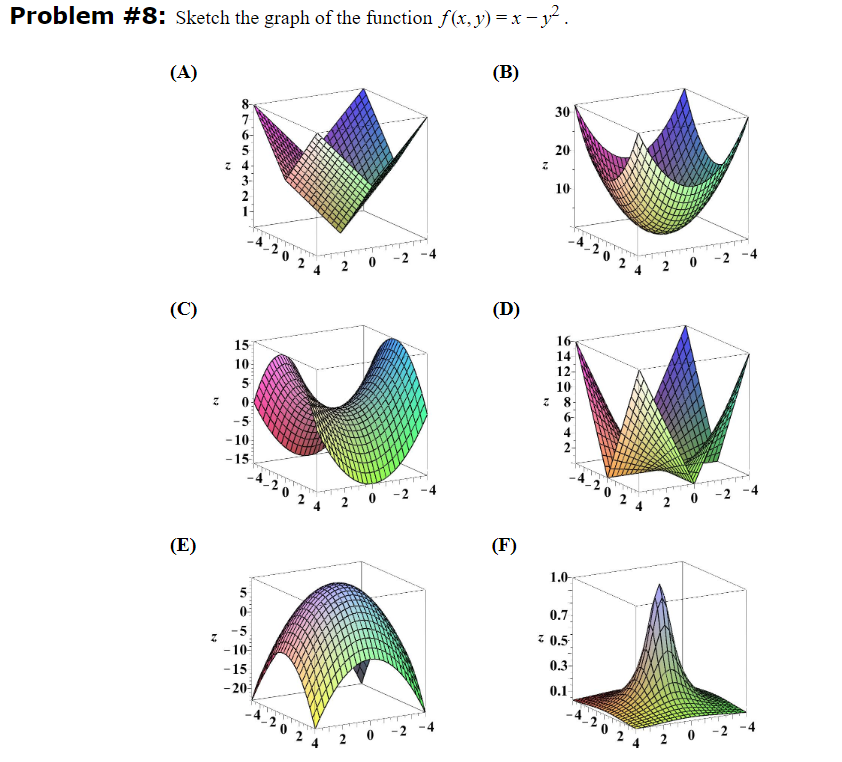



Solved Problem 8 Sketch The Graph Of The Function F X Y Chegg Com




File 3d Graph X2 Xy Y2 Png Wikimedia Commons




A Plot Of The Data F X Y Xe X2 Y2 Documentclass 12pt Minimal Download Scientific Diagram




Solutions To Implicit Differentiation Problems



2



Quadratics Graphing Parabolas Sparknotes




Content The Concept Of A Function
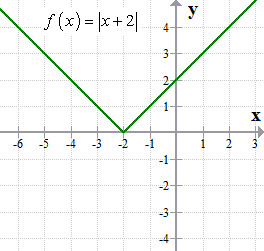



Inverse Of Absolute Value Function Chilimath



Critical Points Of Functions Of Two Variables
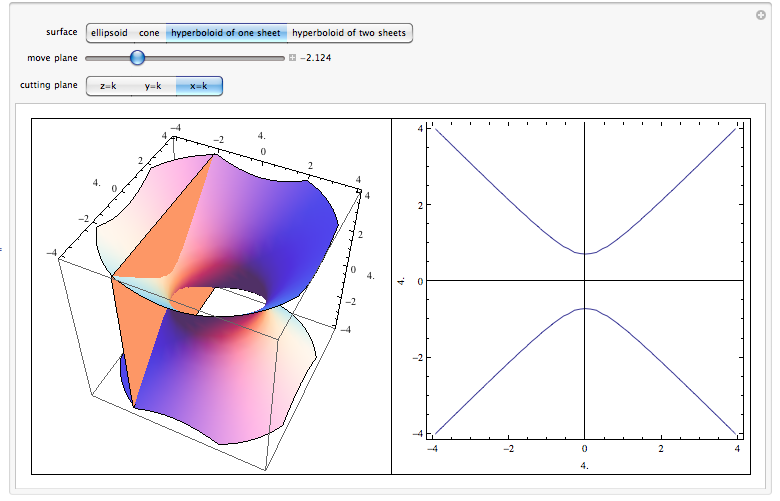



Level Surfaces




If F X Y 9 X 2 Y 2 If X 2 Y 2 Leq9 And F X Y 0 If X 2 Y 2 9 Study What Happens At 3 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange



2



What Is The Graph Of X 2 Y 3 X 2 2 1 Quora



1
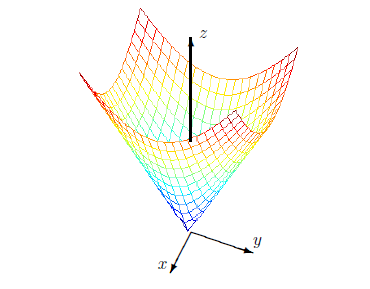



Chapter 8 The Gradient And Linear Approximation Calculus And Analysis
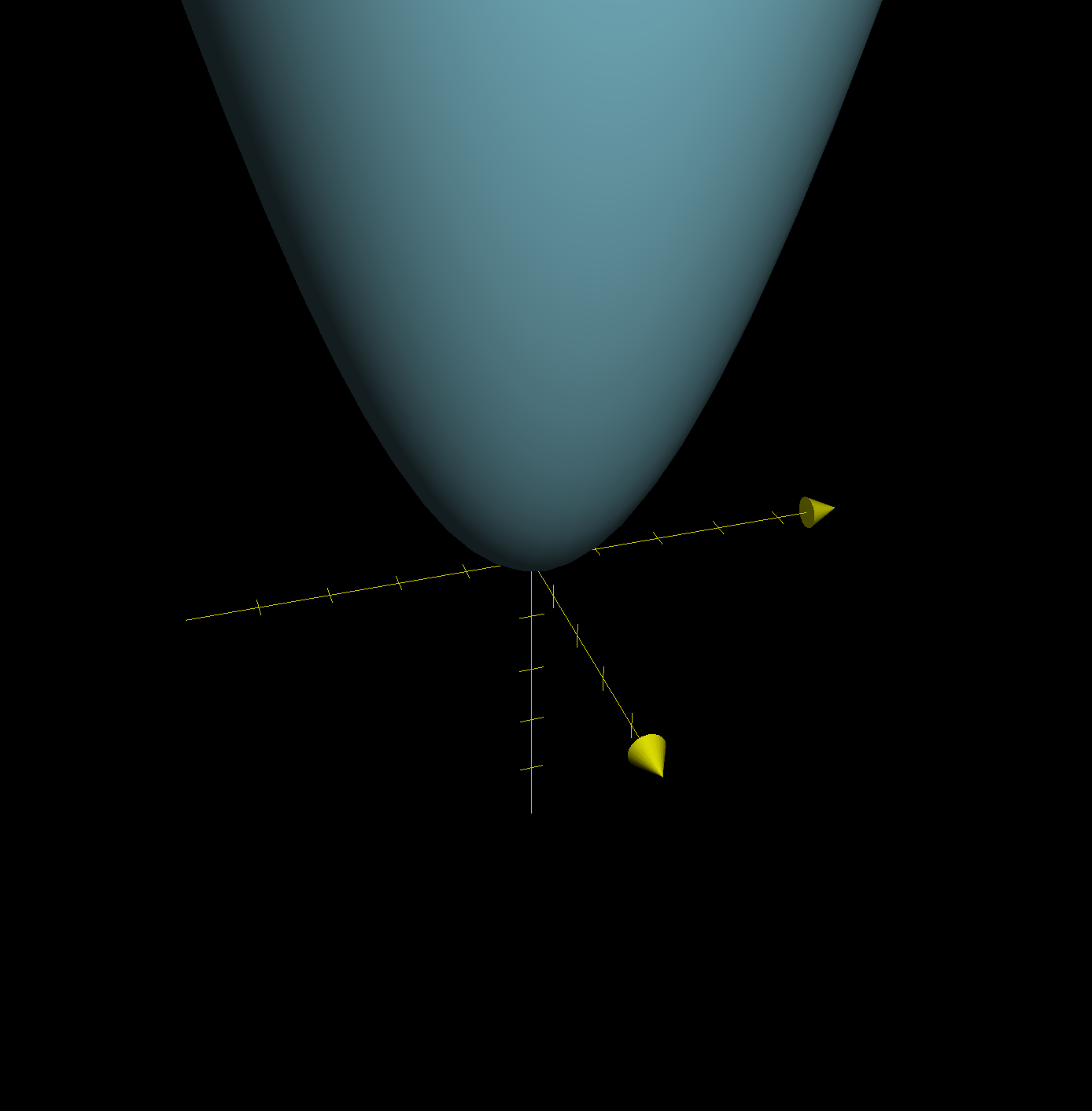



Contour Maps Article Khan Academy



0 3 Visualizing Functions Of Several Variables




Solved Match The Function With Its Graph F X Y X Chegg Com




Functions Of Several Variables Calculus
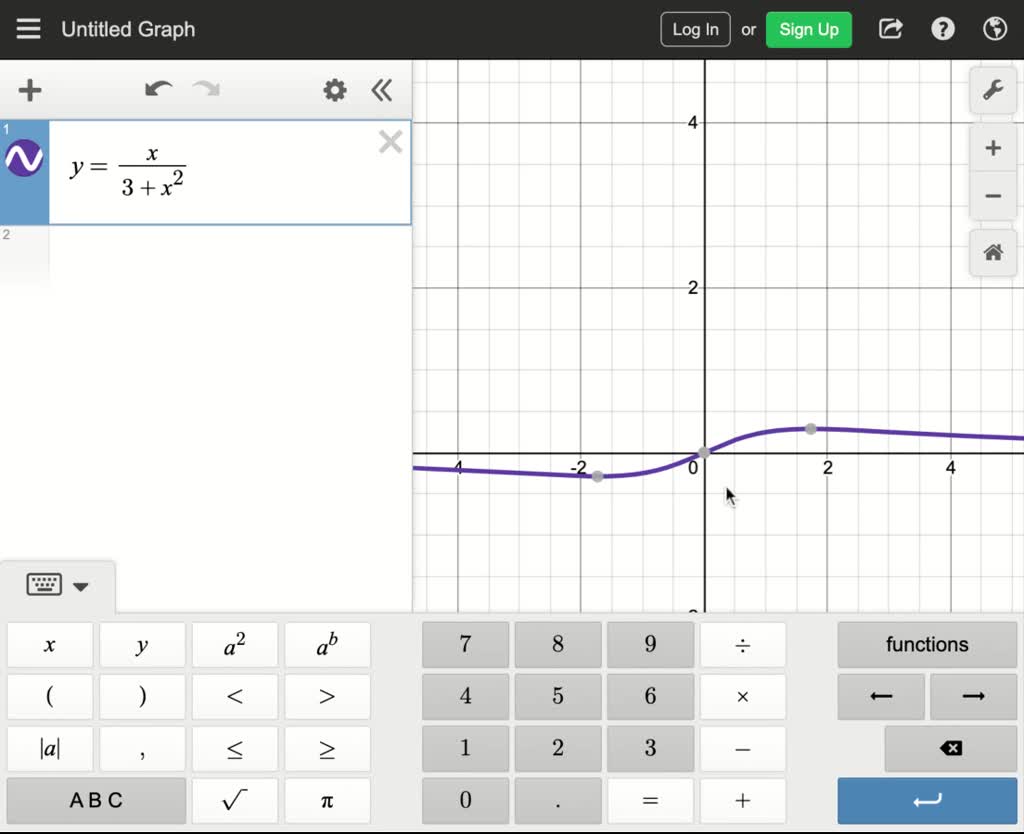



Solved Sketch The Graph Of The Fuction A F X Y X B F X Y 6 2x 3y C F X Y Sqrt 4 X 2 2y 2 What Symmetries Does The Graph Have
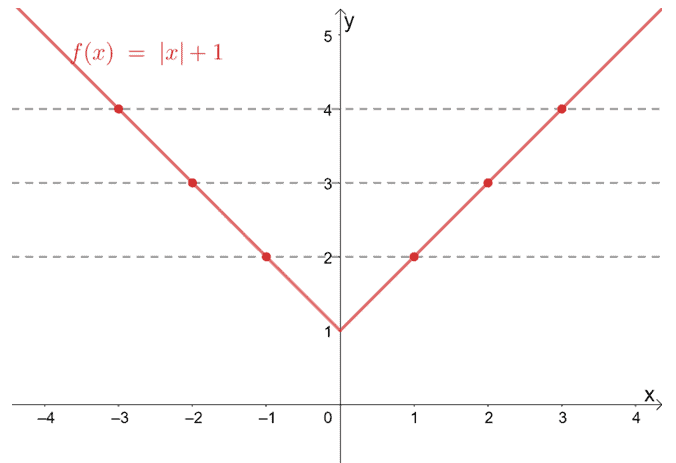



One To One Function Explanation Examples




Solved Graph The Functions Below F X Y X2 Y2 Chegg Com




Multivariable Calculus F X Y X Ln Y 2 X Is A Function Of Multiple Variables It S Domain Is A Region In The Xy Plane Ppt Download
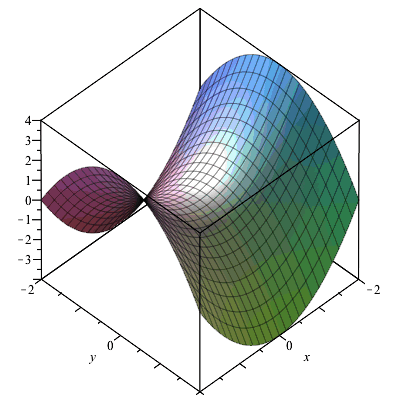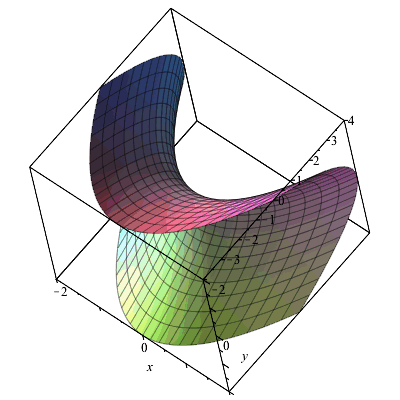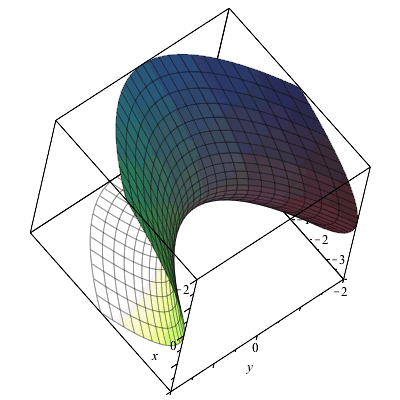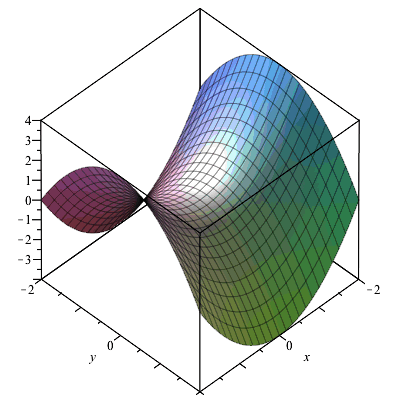



Partial Derivatives Gradients And Plotting Level Curves




Graphing 3d Graphing X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Intro To Graphing 3d Youtube
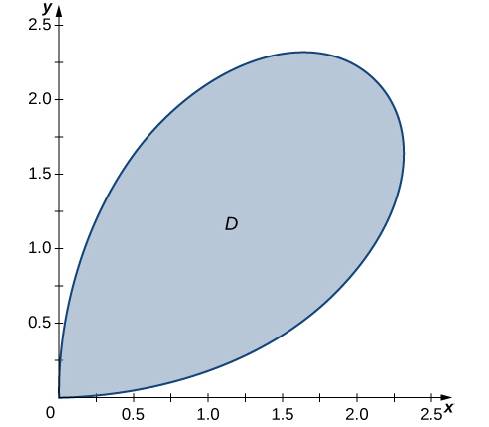



Determine The Average Value Of The Function F X Y X 2 Y 2 Over The Region D Bounded By The Polar Curve R 3 Sin 2 8 Where 0 8 P 2 Following Graph Bartleby



Adell1011 Weebly Com



1
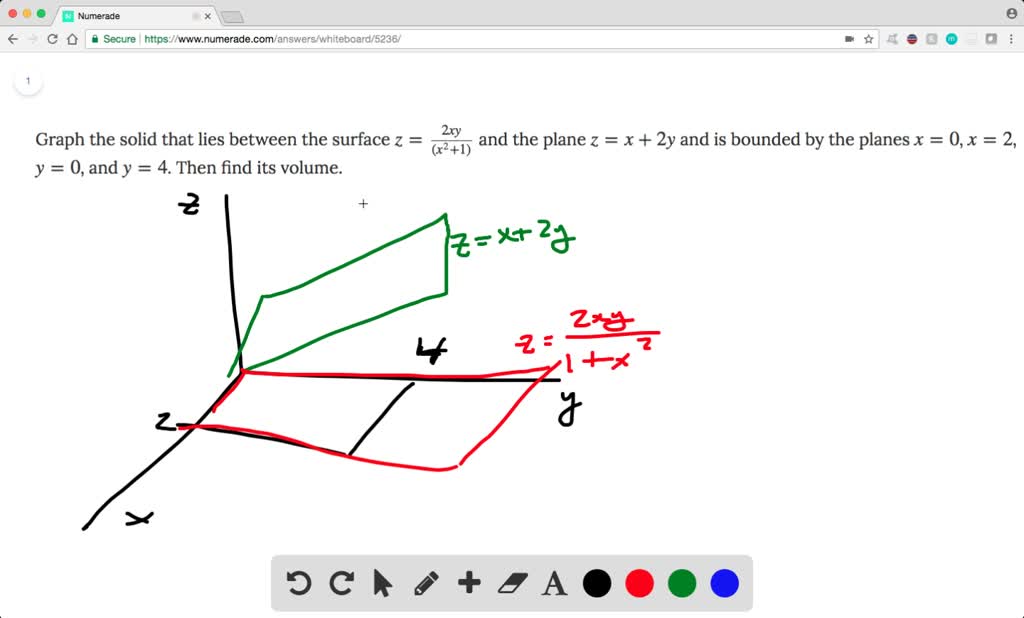



Solved Find The Volume Of The Solid Bounded Above By The Surface Z F X Y And Below By The Plane Region R F X Y 2 X Y R Is The Triangle Bounded By Y 2 X
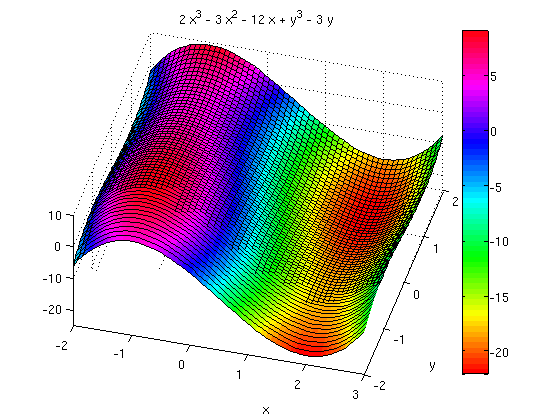



Maxima And Minima Of Functions Of 2 Variables



Surfaces Part 2



Surfaces Part 2




Use A Graph Or Level Curves Or Both To Find The Local Maximum And Minimum Values As Well As Saddle Points Of F X Y 9 X Y E X 2 Y 2 Then Use Calculus To



12 2 Graphs Of Functions Of Two Variables Visualizing A Flip Ebook Pages 1 16 Anyflip Anyflip



Graph Of X Y




Ch1 Graphs Y Axis X Axis Quadrant I Quadrant Ii Quadrant Iii Quadrant Iv Origin 0 0 6 3 5 2 When Distinct Ppt Download



12 2 Graphs Of Functions Of Two Variables Visualizing A Flip Ebook Pages 1 16 Anyflip Anyflip
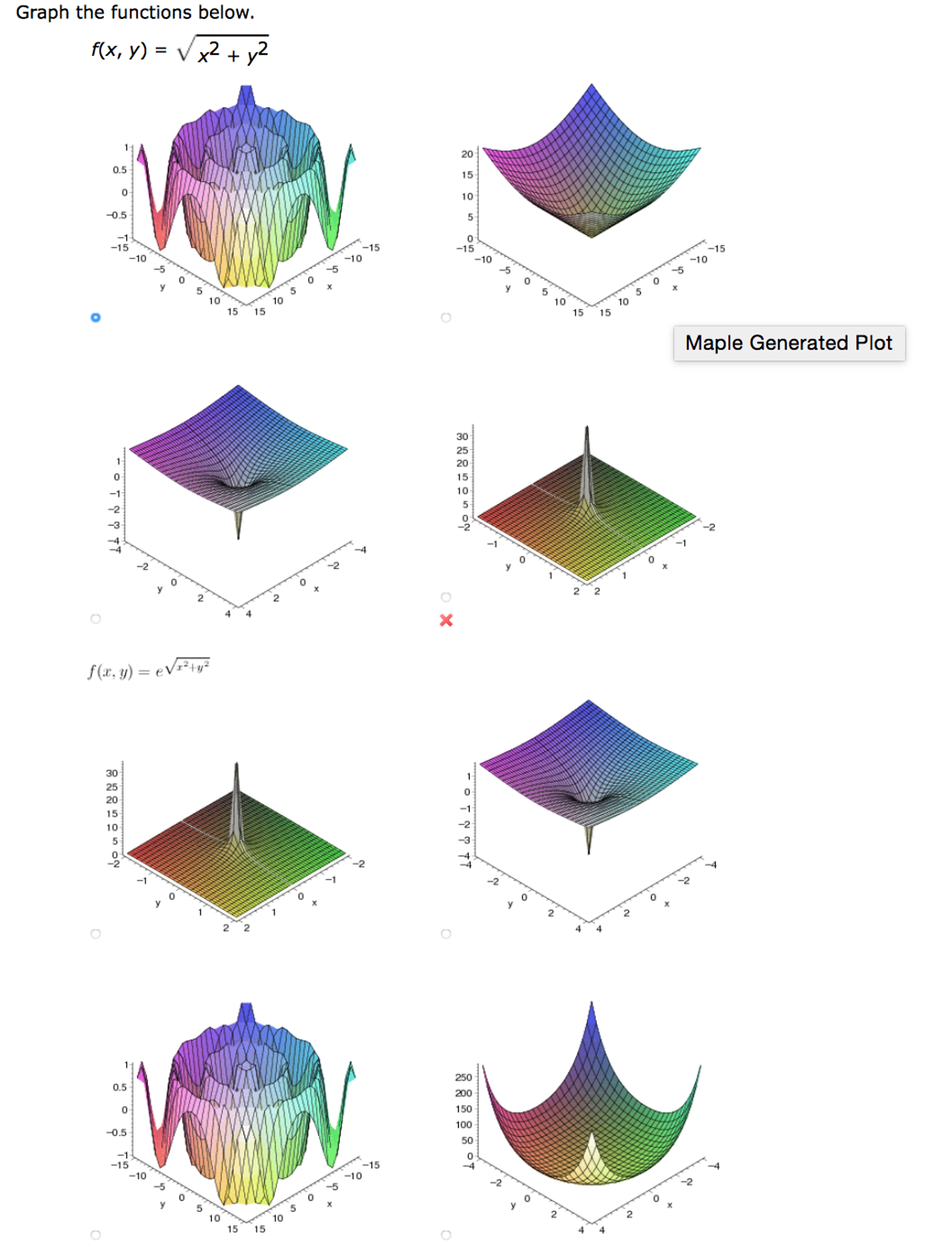



Solved Graph The Functions Below F X Y Squareroot X 2 Chegg Com



Examples Friday Feb 21


